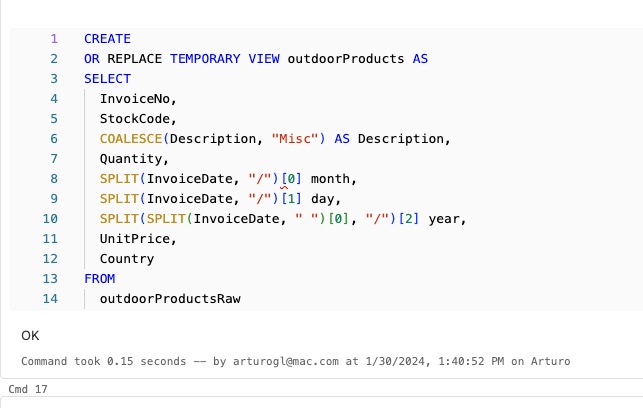
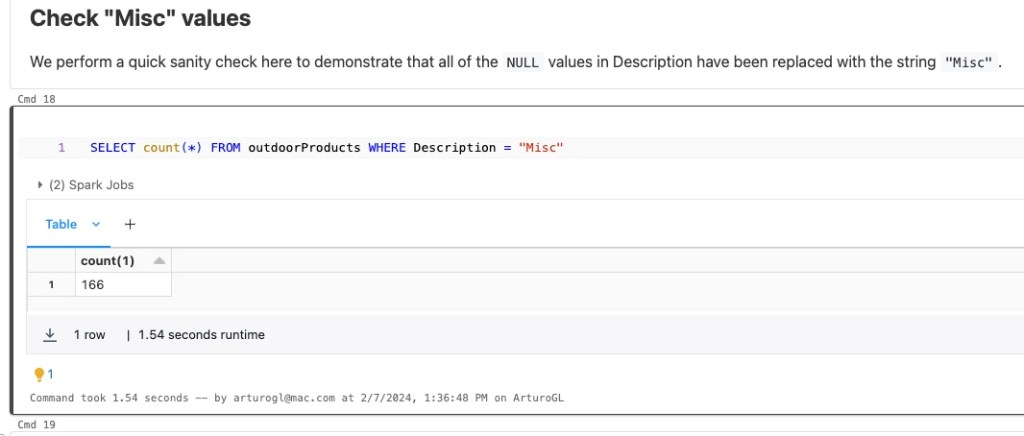
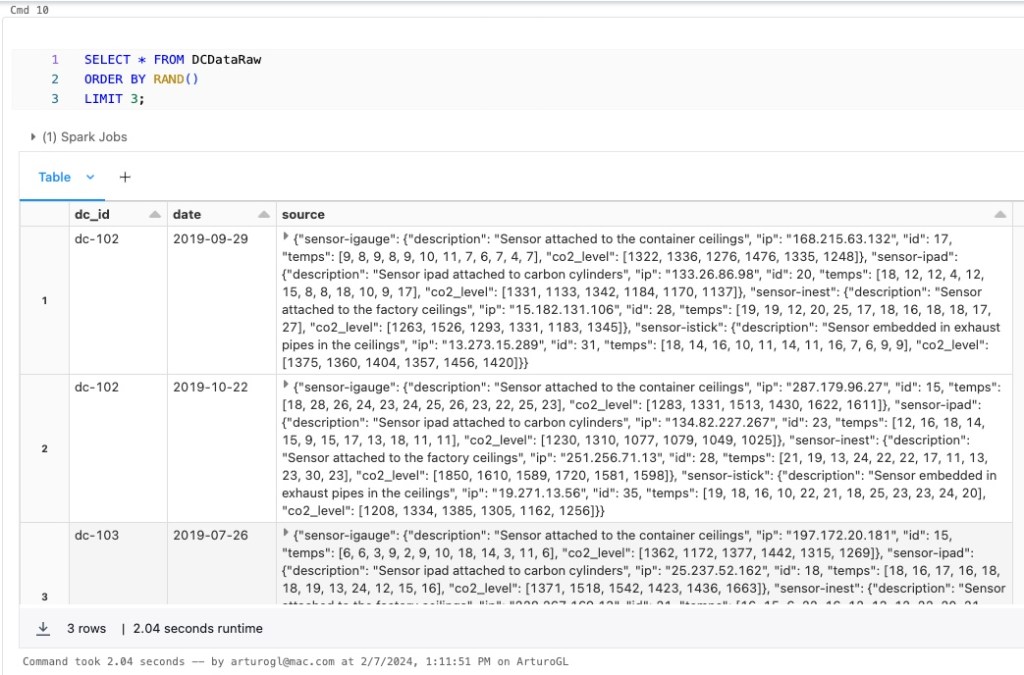
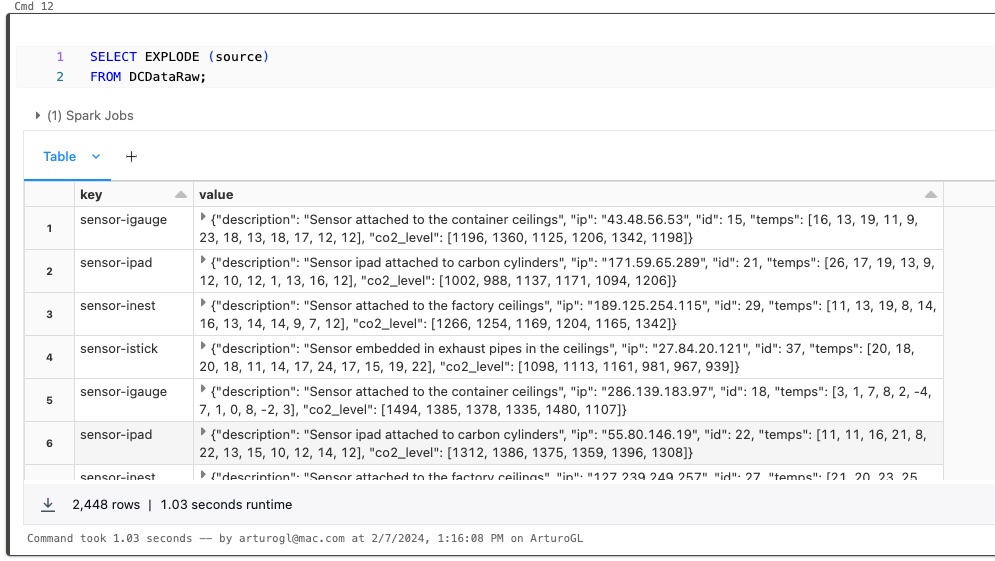
o create a table in Databricks using an external PostgreSQL data source, you can use the CREATE TABLE SQL statement with the USING clause to specify the data source. Here’s a basic example:
CREATE TABLE your_table_name
USING jdbc
OPTIONS (
url 'jdbc:postgresql://your_postgresql_host:port/your_database',
dbtable 'your_table_in_postgresql',
user 'your_username',
password 'your_password'
);
In this SQL statement:
your_table_nameis the name you want to assign to your table in Databricks.jdbcspecifies that you’re using the JDBC data source.urlis the JDBC connection URL for your PostgreSQL database.dbtableis the name of the table in your PostgreSQL database that you want to create a Databricks table from.useris the username to connect to your PostgreSQL database.passwordis the password associated with the username.
Replace the placeholders (your_...) with your actual values.
Make sure you have the appropriate JDBC driver installed in your Databricks cluster. You can upload the JDBC driver JAR file to your cluster’s storage or use Maven coordinates if the driver is available on Maven repositories.
Here’s an example using Maven coordinates for the PostgreSQL JDBC driver:
CREATE TABLE your_table_name
USING jdbc
OPTIONS (
url 'jdbc:postgresql://your_postgresql_host:port/your_database',
dbtable 'your_table_in_postgresql',
user 'your_username',
password 'your_password',
driver 'org.postgresql.Driver'
);
Replace org.postgresql.Driver with the appropriate driver class name for your PostgreSQL JDBC driver.
After running this SQL statement in a Databricks notebook or SQL cell, the table your_table_name will be created in Databricks, and its schema and data will be synchronized with the specified table in your PostgreSQL database.